Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly transforming transportation in the United States. As more people shift from petrol and diesel cars to electric models, one question continues to dominate buyer and owner concerns: How long does it take to charge an EV? Understanding EV charging time comparison in the USA is essential for making informed decisions, whether you are buying your first electric car or upgrading to a newer model.
Charging time is not the same for every EV. It depends on several factors such as battery size, charging level, charging station power, vehicle technology, and even environmental conditions. This detailed guide explains EV charging times in the USA using real-world comparisons, simple explanations, and practical examples.
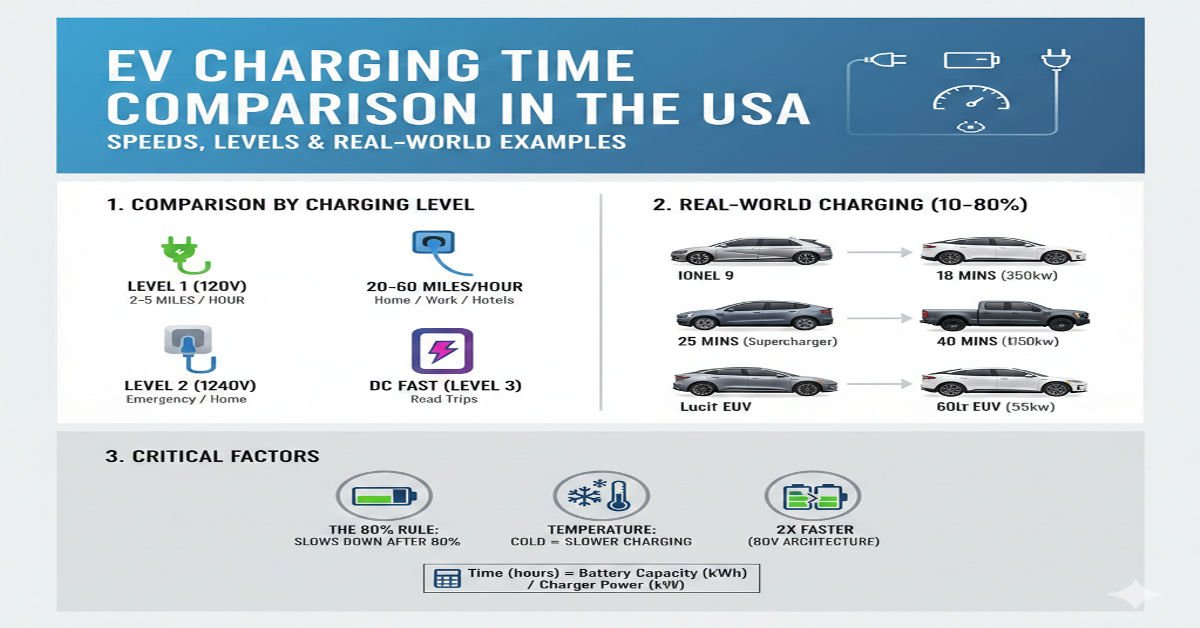
Understanding EV Charging Basics in the USA
Before comparing charging times, it is important to understand how EV charging works in the United States. EV charging is classified into three main levels, each offering different speeds and use cases.
EV Charging Levels Explained
| Charging Level | Power Output | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 120V | Home charging with standard wall outlet |
| Level 2 | 240V | Home chargers and public charging stations |
| DC Fast Charging | 400V–900V | Highway fast charging and commercial stations |
Each charging level significantly affects how long your EV takes to recharge.
Level 1 Charging Time Comparison (USA)
Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet, similar to what powers common home appliances. It is the slowest charging option and is typically included with most EV purchases.
Average Level 1 Charging Times
| EV Type | Charging Speed | Time for Full Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Small EV (40 kWh battery) | 3–5 miles/hour | 24–36 hours |
| Mid-size EV (60 kWh battery) | 3–5 miles/hour | 36–48 hours |
| Large EV (100 kWh battery) | 3–5 miles/hour | 60+ hours |
Level 1 charging is best for drivers with very low daily mileage, such as short city commutes. In the USA, it is common in apartments or older homes where upgrading electrical infrastructure may be difficult.
Level 2 Charging Time Comparison in the USA
Level 2 charging is the most popular and practical option for American EV owners. It uses a 240-volt connection, similar to electric dryers or ovens, and is widely available in homes, workplaces, malls, and public parking areas.
Average Level 2 Charging Times
| EV Battery Size | Charging Speed | Full Charge Time |
|---|---|---|
| 40 kWh | 25–30 miles/hour | 6–8 hours |
| 60 kWh | 25–30 miles/hour | 8–10 hours |
| 75 kWh | 25–30 miles/hour | 10–12 hours |
| 100 kWh | 25–30 miles/hour | 12–16 hours |
For most EV owners in the USA, Level 2 charging overnight at home is sufficient. This method balances speed, cost, and battery health, making it the most recommended charging option.
DC Fast Charging Time Comparison (USA)
DC fast charging, also known as Level 3 charging, is designed for long-distance travel. These chargers bypass the vehicle’s onboard charger and supply direct current straight to the battery.
Typical DC Fast Charging Times
| Charger Power | Time to Charge 20%–80% |
|---|---|
| 50 kW | 45–60 minutes |
| 100 kW | 30–45 minutes |
| 150 kW | 20–30 minutes |
| 250 kW+ | 15–25 minutes |
In the USA, most highway charging stations operated by networks like Electrify America, Tesla Superchargers, and EVgo use DC fast charging.
EV Model-Wise Charging Time Comparison in the USA
Different EV models charge at different speeds depending on battery size and charging technology.
Popular EV Charging Time Comparison
| EV Model | Battery Size | Level 2 Time | DC Fast (20%–80%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Model 3 | 60 kWh | 8–9 hours | 20–25 minutes |
| Tesla Model Y | 75 kWh | 10–12 hours | 25 minutes |
| Chevrolet Bolt EV | 65 kWh | 9–10 hours | 30–45 minutes |
| Ford Mustang Mach-E | 88 kWh | 11–13 hours | 30–40 minutes |
| Hyundai Ioniq 5 | 77 kWh | 9–10 hours | 18–22 minutes |
This comparison clearly shows that charging time in the USA varies widely even among popular models.
Factors Affecting EV Charging Time in the USA
EV charging time is influenced by more than just charger type. Understanding these factors helps drivers manage charging more efficiently.
Battery Capacity
Larger batteries take longer to charge, but they also offer longer driving range.
Charger Power Output
A high-power charger reduces charging time, but only if the EV supports that power level.
Vehicle Charging Limit
Some EVs cap charging speeds to protect battery health.
Battery State of Charge
Charging slows significantly after 80%, especially with DC fast charging.
Weather Conditions
Cold weather common in northern US states can increase charging time by 10–30%.
Home Charging vs Public Charging Time Comparison
| Charging Location | Speed | Convenience | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Level 1 | Very Slow | High | Low |
| Home Level 2 | Moderate | Very High | Low |
| Public Level 2 | Moderate | Medium | Medium |
| DC Fast Charging | Very Fast | Medium | High |
Most EV owners in the USA rely on home Level 2 charging for daily needs and DC fast charging for road trips.
EV Charging Time Cost Comparison in the USA
Charging speed also affects cost.
| Charging Type | Average Cost per kWh | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Home Charging | $0.12–$0.18 | Daily charging |
| Public Level 2 | $0.20–$0.30 | Occasional use |
| DC Fast Charging | $0.35–$0.60 | Long trips |
Faster charging usually costs more, which is why most Americans prefer charging overnight at home.
Real-World EV Charging Time Scenarios
Daily Commuter
A driver traveling 40 miles per day can fully recharge overnight using a Level 2 charger in 2–3 hours.
Weekend Road Trip
DC fast charging can add 200 miles of range in about 20–30 minutes, ideal for highway stops.
Apartment Resident
Level 1 charging may work if daily driving is under 30 miles, but charging time remains long.
EV Charging Time Comparison for Road Trips in the USA
Long-distance EV travel depends heavily on charging speed and station availability.
| Charging Stop | Average Stop Time | Range Added |
|---|---|---|
| DC Fast Charger | 20–30 minutes | 150–250 miles |
| Level 2 Charger | 1–2 hours | 50–80 miles |
This comparison shows why DC fast charging is essential for cross-state travel in the USA.
Battery Health and Charging Speed Balance
Fast charging is convenient but frequent use may slightly degrade battery life over time. Experts recommend:
-
Daily use of Level 2 charging
-
Limiting DC fast charging to trips
-
Charging between 20% and 80% for longevity
This balanced approach ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Future EV Charging Time Improvements in the USA
Charging times are expected to decrease significantly with technological advancements.
| Technology | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| 800V battery systems | Faster charging |
| Solid-state batteries | Reduced charging time |
| Expanded fast-charging networks | Better accessibility |
| Smart charging software | Optimized charging speed |
The USA is investing heavily in EV infrastructure, making charging faster and more convenient every year.
Trust and Reliability of Charging Time Estimates
Charging time estimates provided by manufacturers are based on ideal conditions. Real-world results may vary depending on:
-
Charger availability
-
Grid power limitations
-
Battery temperature
-
Software updates
Understanding these variables builds trust and realistic expectations for EV owners.
EV Charging Time Comparison Summary
| Charging Method | Best Use Case | Time Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Emergency or low use | Very Low |
| Level 2 | Daily home charging | High |
| DC Fast | Long trips | Very High |
For most drivers in the USA, Level 2 charging offers the best balance of speed, cost, and convenience.
Final Thoughts
EV charging time comparison in the USA shows that electric vehicles are more practical than ever before. With expanding infrastructure, faster charging technologies, and improved battery systems, charging an EV is no longer a major inconvenience. Understanding charging levels, vehicle compatibility, and real-world scenarios helps users make confident decisions.
As EV adoption continues to grow across the United States, charging times will only get shorter, making electric vehicles a smarter and more sustainable choice for the future.
2 thoughts on “EV Charging Time Comparison in the USA”